In precision applications ranging from cinema projection to surgical lighting, xenon lighting is a critical functional component that can influence system accuracy, safety, and performance.
While LEDs dominate most mainstream lighting systems today, xenon lighting remains a top choice in markets where specific optical performance characteristics, rapid response, and dependability under extreme conditions are crucial.
This article outlines the core benefits of xenon lighting, with a deeper look at what engineers need to consider when specifying or sourcing xenon gas for advanced medical, industrial, and scientific systems.
What is Xenon Lighting?
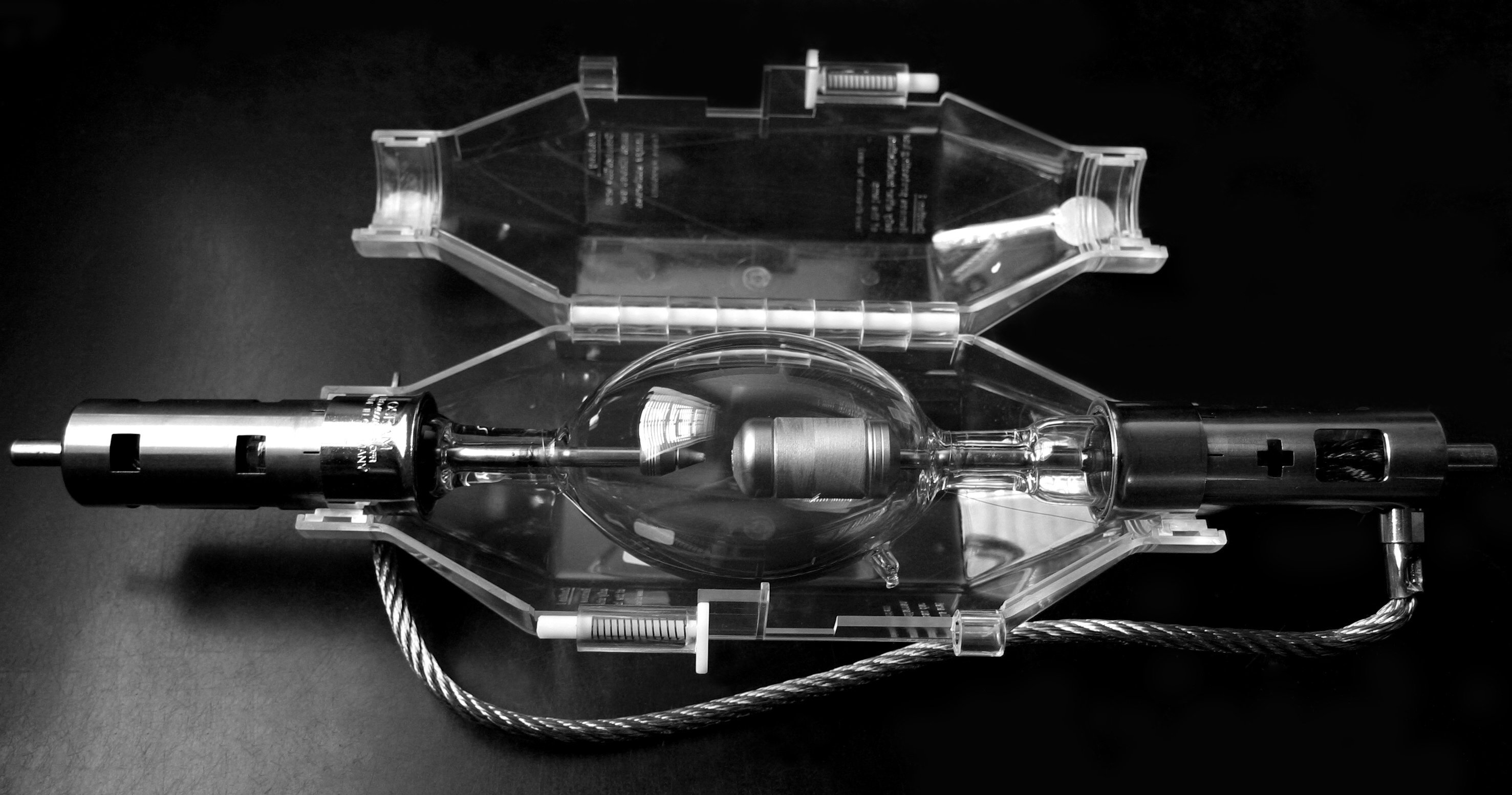
Xenon lighting systems use an electrical discharge through xenon gas to produce an intense, broad-spectrum light output. Unlike halogen lamps (which rely on a heated filament) or LEDs (which generate light through semiconductor emission), xenon lamps create a high-energy arc that delivers a bright, white light with excellent color rendering and rapid response characteristics.
Engineers value xenon lighting for several core properties:
- High-intensity, broad-spectrum output suitable for precision optical work
- Strong color rendering, which supports tasks requiring accurate visual differentiation
- Instant or near-instant response, beneficial for signaling, strobes, and high-speed imaging
Advantages of Xenon Lighting
Xenon lighting remains a critical contributor to specialized systems, particularly where LED performance may not fully meet operational needs. Engineers typically consider xenon when one or more of the following factors apply.
- A Need for High-Intensity Arc Output: Applications that require a dense, high-energy light source (such as projection, strobes, or surgical illumination), where a single point-source arc is advantageous.
- Superior Color Rendering Requirements Under Demanding Conditions: Environments like operating rooms or inspection systems need light that accurately represents color across the visible spectrum.
- Broad Spectral Requirements Beyond Visible Light: Systems such as UV disinfection units, spectroscopy tools, or scientific instruments rely on xenon’s wide spectral range, including UV and infrared components.
- Extreme Operating Environment: Aircraft beacons, emergency strobes, and other high-stress systems benefit from xenon’s reliability under vibration, temperature swings, and environmental exposure.
- Instantaneous or Fast-Pulse Operation: Xenon’s rapid ignition and pulse capability can outperform LED response characteristics in certain signaling and high-speed optical applications.
- Thermal or Optical Constraints That Favor an Arc Source: Some optical architectures are designed around the geometry and emission pattern of a xenon arc, making it a better fit than distributed LED emitters.
Key Advantages of Xenon Lights in Specialized Applications
LEDs have largely superseded xenon lighting systems in certain mainstream consumer use-cases, like high-end vehicle headlights. However, xenon remains a leading choice across many specialized or industrial applications.
Medical
Xenon’s bright, continuous-spectrum output supports the visual precision required in surgical and diagnostic settings. Its light quality helps clinicians distinguish subtle variations in tissue and anatomy, and the stable arc output integrates well into sterile, high-reliability operating environments.
Cinema Projection
Xenon short-arc lamps remain widely used in digital cinema projectors because they deliver a very bright, highly concentrated point source suitable for large-format screens. Their broad spectral output, strong color characteristics, and ability to maintain stable brightness over the lamp’s service life make them a dependable choice for theaters.
While laser-based cinema projection systems are a rapidly maturing alternative technology, xenon-based projectors remain valued for their proven operating characteristics and field serviceability.
Industrial and Aerospace
In aerospace and industrial signaling, xenon lamps provide the intense, momentary bursts of light needed for strobes, beacons, and safety indicators. Their ability to perform consistently under vibration, temperature swings, and long operating cycles makes them well-suited to aircraft lighting and other heavy-duty systems.
Specialty and Scientific
Research tools, spectroscopy equipment, and UV-based systems depend on xenon for its broad spectral range, especially in the ultraviolet portion. This allows engineers to design instruments that require controlled wavelength output, from analytical measurements to targeted UV exposure in lab or disinfection settings.
Xenon Lighting Design Considerations for Engineers
- Electrical Requirements: Xenon lamps require a dedicated power system capable of delivering a high-voltage ignition pulse and stable operating current. Proper ballast integration can enable consistent arc performance and helps maintain expected lamp life.
- Thermal Management: Xenon arc sources generate concentrated heat at the lamp envelope and surrounding components. Systems must be designed with adequate airflow or heat dissipation to maintain safe operating temperatures and prevent premature wear.
- Optical Design: Because xenon functions as a compact, high-brightness point source, optical performance depends on how the lamp is paired with reflectors, lenses, or light guides. Engineers must select optical components that maintain uniform output and reduce UV spillover where necessary.
- Lifetime and Maintenance: Lamp life varies by operating power and duty cycle, and systems should plan for routine replacement as part of normal maintenance. Stable electrical regulation and controlled temperature conditions help maintain consistent performance over the lamp’s service life.
- A High-Purity Gas Supply: Xenon lamp reliability is directly influenced by the purity of the gas used in manufacturing. Impurities can shorten lamp life or disrupt arc stability. Messer supports specialty lighting and electronics customers with high-purity xenon produced and filled in the U.S., available in standard CGA, DIN, or JIS cylinder configurations.
Safety and Compliance Factors
Xenon lamps produce UV, visible, and infrared radiation, and system housings are typically designed to shield operators from direct UV exposure. Optical filters or UV-absorbing components may also be included when the application requires tighter control over the emitted spectrum.
Beyond lamp-level considerations, xenon itself is supplied as a high-pressure gas, and proper handling is essential for safe system integration. Engineers working with xenon cylinders should follow standard compressed-gas protocols, including:
- Securing cylinders during storage and use,
- Ensuring proper valve connections,
- And incorporating regulators and downstream components rated for the required pressures.
Users can review the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for xenon to understand specific hazards, recommended PPE, and safe handling practices.
ROI and Application Fit
Compared to LED systems, xenon lighting typically carries a higher operating cost due to scheduled lamp replacement and the electrical requirements of discharge lamps. For most general-purpose lighting, LEDs offer better long-term efficiency.
However, in performance-critical or tightly defined optical applications, xenon can provide strong value.
Moving forward, LEDs will continue to dominate mainstream platforms, but xenon is likely to maintain steady demand in niche applications where its optical and operational properties are uniquely suited to the task.
Learn More About Sourcing High-Purity Xenon Gas for Lighting
Messer supports xenon lighting manufacturers with a U.S.–based supply chain. Our high-purity xenon is produced, purified, and filled domestically. Each cylinder is prepared and quality-checked to meet the requirements of specialty lighting and optical equipment manufacturers.
We also work closely with customers across cinema, medical, aerospace, and scientific markets to understand their system requirements and facilitate xenon that aligns with their performance and integration needs. Whether supporting prototype development or ongoing production, Messer’s specialty gas knowledge and logistics can help keep critical lighting systems operating as required.
To discuss xenon supply options or request technical guidance, contact the Messer specialty gases team.


Comments
Messer makes no warranty of any kind with respect to the subject matter, the completeness, or accuracy of this blog. Messer is not responsible for any actions (or lack thereof) taken as a result of relying on or in any way using information contained in this blog. In no event shall Messer be liable for any damages resulting from reliance on or use of information in this blog. Readers should take advice from a qualified professional when dealing with specific situations. Descriptions of, or references or access to, other publications within this blog do not imply endorsement of those publications. This blog may contain technical inaccuracies and changes to the information may be made at any time.
Gas products are hazardous. The use or misuse of gas products involves serious risks, including injury, disability and death. Users of gas products must use the Safety Data Sheets for the gas products to warn their employees and others who are exposed to the gas products or hazards associated with such products.